The Operation of Bitcoin Mining: A Comprehensive Guide
Operation of Bitcoin Mining: Bitcoin mining is a crucial process in the world of cryptocurrency. It’s the mechanism through which new bitcoins are created and transactions are validated on the blockchain network. In this article, we’ll break down how Bitcoin mining works, Ethereum Reaches New Heights A Complete Guide the technology behind it, and its significance in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
What is Bitcoin Mining?
Bitcoin mining refers to the process of validating and adding transactions to the Bitcoin blockchain. A decentralized ledger that records all transactions. Mining involves solving complex mathematical problems through a process called “proof of work.” Miners use powerful computers to perform this process, and in return, they are rewarded with newly minted bitcoins and transaction fees.
How Does Bitcoin Mining Work?
The process of Bitcoin mining can be broken down into several steps:
- Transaction Verification: When someone sends or receives Bitcoin, the transaction needs to be verified. This is done by miners who group these transactions into a “block.”
- Proof of Work (PoW): Miners compete to solve a complex cryptographic puzzle that requires significant computational power. This process is known as proof of work. The goal is to find a hash (a unique digital signature) that satisfies specific conditions set by the Bitcoin network.
- Block Addition: The first miner to solve the puzzle broadcasts the solution to the rest of the network. Other miners validate the solution, and if it is correct, the new block is added to the blockchain. This confirms that the transactions in that block are legitimate.
- Reward: Once a block is successfully added to the blockchain, the miner is rewarded with a certain number of bitcoins. This is known as the “block reward.” The current reward is 6.25 bitcoins, but this amount halves approximately every four years, in an event known as the “halving.”
The Role of Mining Pools
Mining alone can be highly competitive, requiring vast amounts of computational power and electricity. To increase the chances of earning rewards, many miners join mining pools. These are groups of miners who combine their computational resources to solve cryptographic puzzles more quickly. The rewards earned from successfully mining a block are then distributed among the pool members based on the computational power they contributed.
The Technology Behind Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin mining relies on specialized hardware known as ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits). These machines are designed specifically for the purpose of mining cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. In the early days of Bitcoin, miners could use regular PCs or graphics cards (GPU mining), but as the network grew, the difficulty level of mining increased. Making it nearly impossible to mine profitably without specialized hardware.
ASIC miners are much more efficient than general-purpose hardware, but they also consume a lot of energy. This is one of the reasons why mining has become concentrated in regions where electricity is cheap.
Energy Consumption and Environmental Impact
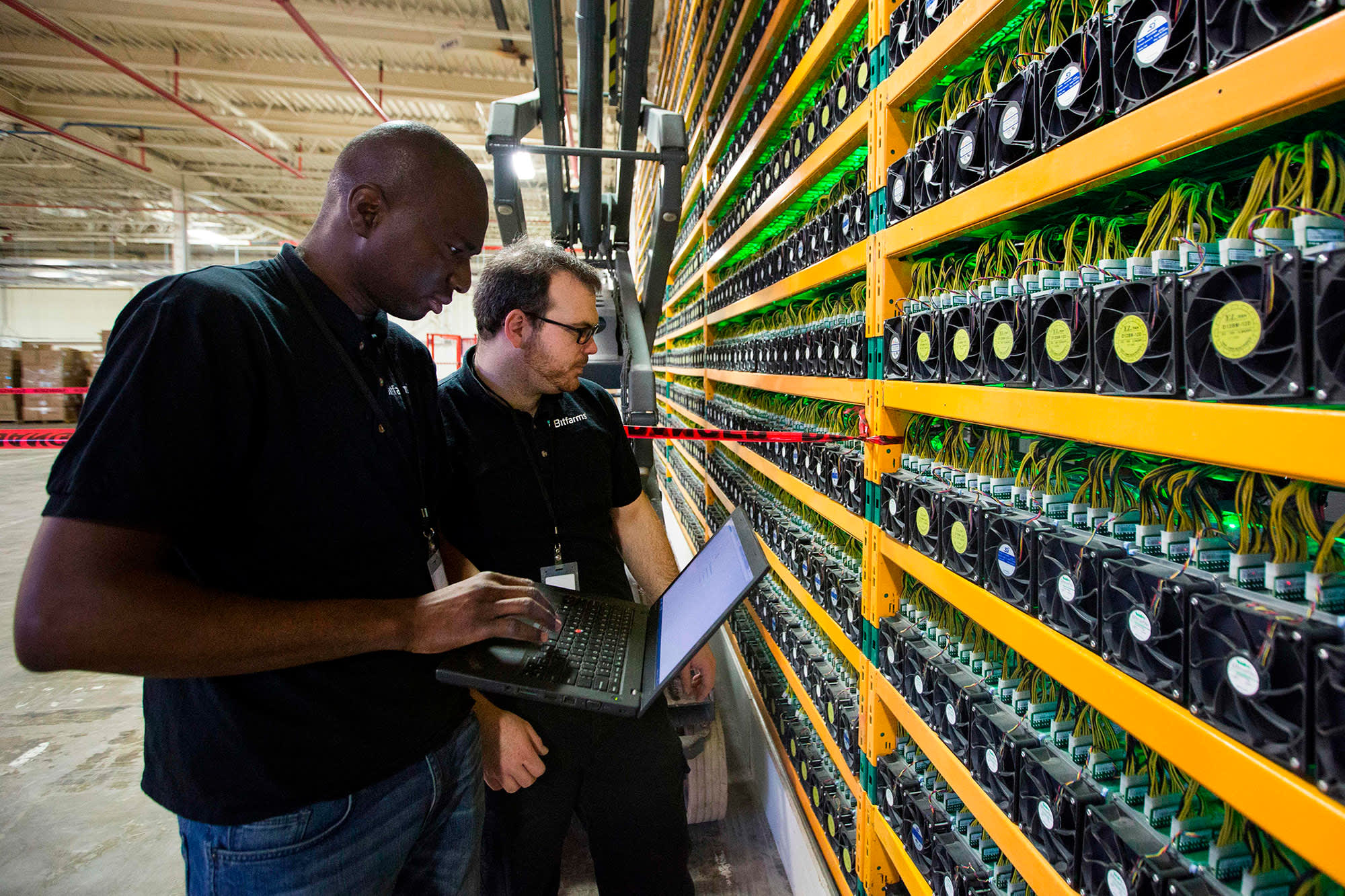 Bitcoin mining has been criticized for its energy consumption. Mining requires a tremendous amount of computational power. Which translates into high electricity usage. Some estimates suggest that Bitcoin mining consumes as much electricity as entire countries.
Bitcoin mining has been criticized for its energy consumption. Mining requires a tremendous amount of computational power. Which translates into high electricity usage. Some estimates suggest that Bitcoin mining consumes as much electricity as entire countries.
To address this concern, there has been a push toward using renewable Operation of Bitcoin Mining energy sources in mining operations. Many mining farms are now located in areas with abundant renewable energy. Such as hydroelectric power from rivers or wind energy from turbines.
The Bitcoin Halving
A key feature of Bitcoin’s monetary policy is the halving event, which occurs every 210,000 blocks, or roughly every four years. During this event, the reward that miners receive for adding a block to the blockchain is cut in half. This reduces the rate at which new bitcoins are generated and helps control inflation. The most recent halving occurred in 2020, reducing the block reward from 12.5 to 6.25 bitcoins.
The halving creates scarcity, which can influence the price of Bitcoin. Historically, halvings have been associated with significant increases in the price of Bitcoin as the supply of new Bitcoins slows down.
Why is Bitcoin Mining Important?
- Securing the Network: Mining is essential for the security of the Bitcoin network. Miners validate transactions, making it nearly impossible to alter the blockchain without controlling more than 50% of the network’s computational power, a feat known as a “51% attack.”
- Decentralization: Bitcoin mining ensures that the network remains decentralized. Anyone can participate in mining, and the network does not rely on a central authority to verify transactions.
- New Bitcoin Creation: Through mining, new bitcoins are introduced into circulation. This process ensures that Bitcoin’s supply is limited and distributed over time, which helps maintain its value.
- Transaction Fees: In addition to the block reward, miners also earn transaction fees. These fees come from the users who want to have their transactions included in the blockchain.
Conclusion
Bitcoin mining is the backbone of the Bitcoin network. It is a process that involves validating transactions, securing the network, and introducing new bitcoins into circulation. While it requires significant computational resources and energy, it also plays a crucial role in ensuring the integrity Operation of Bitcoin Mining and decentralization of the cryptocurrency ecosystem. As the Bitcoin network continues to grow, the process of mining will evolve, but it remains a fundamental part of what makes Bitcoin decentralized and secure.
[sp_easyaccordion id=”5238″]