As a Trader, How Can I Make Use Of Fundamental Analysis?
As a Trader, How Can I Make Use Of Fundamental Analysis? Investors and traders often turn to fundamental research when determining an asset’s worth. If an asset’s actual cost is not immediately apparent by looking at its market price, fundamental analysis can help you find it by analyzing economic and financial data and other intangibles.
Remember that all the financial items you can trade with Axis—forex, shares, stock indexes, commodities, and cryptocurrency—are amenable to fundamental research.
Key points
- Fundamental analysis examines the social, political, and economic indicators that might affect the price and performance of a financial asset.
- Fundamental analysts look at the economic factors affecting an asset’s performance, while technical analysts look strictly at the price and volume through trading charts.
- There are two types of fundamental analysis: quantitative and qualitative.
What is fundamental analysis?

Before investing, fundamental analysts look at the economic, social, and political factors that can impact the asset’s value and performance. One way to apply this investing strategy is to look into the companies that make or provide a product.
Some examples of what may be covered in this type of business research include hazards, management strategies, financial health, statements, future growth, product performance patterns, and challenges faced by competitors. Determining if a potential investment opportunity is overpriced or underpriced is the main objective of fundamental research.
This kind of analysis is the ideal way to do your homework before investing if you notice that an asset you’re watching is trading at an unusual level and could make money if you buy it. Be mindful that while there may have been an opportunity for gain, there is also a chance that it could lead to loss.
How does fundamental analysis work?
The lens through which fundamental investors see the market is more expansive. The impact of macroeconomic variables, political climate, and interest rates on an asset’s value will be considered.
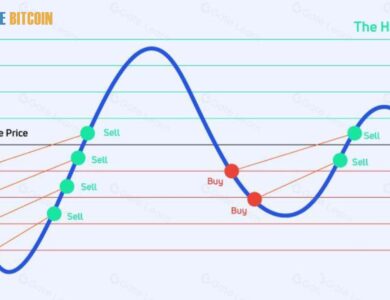
To attempt to forecast future prices based on patterns in the past, technical analysis is primarily concerned with charts that display price changes over time. Technical analysts employ tools such as moving averages, Fibonacci retracement, and support and resistance levels to determine when purchasing or selling an asset is most advantageous.
What’s the difference between fundamental and technical analysis?
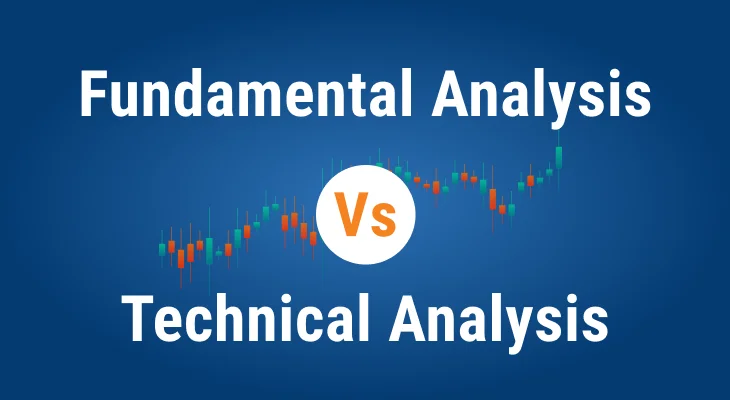
Fundamental analysts can determine if its current price reflects its actual value by analyzing the underlying economic elements that impact an asset’s performance. To carry out the study from a macro-to-micro viewpoint, publicly available data is utilized. To make predictions of pricing, technical analysts examine price and volume charts. In technical analysis, an item’s past price and value are the only factors considered rather than the fundamentals.
In contrast to fundamental research, technical analysis looks at past market data (price and volume, for example) to predict where prices will go. Whereas fundamental analysts place a premium on discovering long-term potential, technical traders rely on momentum and often engage in positions with a shorter period.
What distinguishes quantitative and qualitative fundamental analysis?
There are two types of fundamental factors: quantitative analysis and qualitative analysis.
Quantitative fundamental analysis looks at several items, including financial ratios, market capitalization, interest rate policies, and earnings per share. The quantitative data is determined by the asset you are researching. These statistics are then used to compare against similar instruments or industry averages to determine its profitability.
Qualitative fundamental analysis involves looking at qualitative factors such as management quality, brand recognition, company executives, and proprietary technology. This research relates more to the standard of something than elements that focus solely on numbers, like a company’s revenue or profit margins.
Many fundamental analysts consider that qualitative and quantitative analysis work together to provide a more in-depth analysis.
What quantitative fundamentals should you consider in your analysis?
Below are a few fundamental factors you should consider when looking at any potential investment opportunity through a quantitative lens. Remember that different assets require research of other fundamentals.
- Market capitalisation
- Price ratios (earnings per share, price-earnings ratio, price-earnings growth ratio, and price-book ratio)
- Return on investment ratios (return on assets, return on equity, and profit margin)
- Liquidity ratios (current ratio and quick ratio)
- Leverage ratios (debt-equity ratio and interest coverage ratio)
- Efficiency ratios (asset turnover and inventory turnover)
- The revenue growth rate of the company and its competitors
- Management quality, including insider holdings and past performance in similar positions
- Financial statements (income statement, balance sheets, and cash flow statements)
- GDP, CPI, interest rate policies, unemployment rates, inflation
What qualitative fundamentals should you consider in your analysis?
In the list below, we have elements of qualitative fundamentals that you need to consider when performing this type of asset analysis.
- Company management
- Corporate governance
- Business model
- Competitive advantage and brand recognition
- Industry of the asset (regulations, market share, customer base, competition)
- Competitors (What are the competitors doing? What is their strategy? How does this compare with the company of the asset you are analyzing?)
Many traders conduct both types of analysis when using fundamentals, so neither qualitative nor quantitative analysis is better than the other.
Top-down vs. Bottom-up fundamental analysis
Fundamental analysis is divided into two different schools of thought:
Top-down fundamental analysis
Top-down fundamental analysis uses the market as a whole and looks at how it should change to achieve equilibrium with fundamentals. Since the top-down approach examines the overall market, it is more beneficial for short-term investors who are aiming to make a profit from swings in the market.
Bottom-up fundamental analysis
In contrast, bottom-up fundamental analysis gathers data from separate company analyses and then compiles them into a whole. Long-term investments are typically pursued by bottom-up investors, who, after doing their homework, come up with a solid asset that they think can do well regardless of how the sector as a whole does.
Determining intrinsic value
Determining the asset’s true worth is among the most crucial steps in doing a fundamental analysis. To find out if an asset is priced too high, too low, or about right, traders employ fundamental research. Finding an asset’s worth requires conducting research using a bottom-up financial analysis strategy. Finding investment opportunities inside the industry is the next step for the trader after determining the cost.
Fundamental analysis tools
These are some of the most critical factors you will want to identify and analyze when conducting your fundamental analysis:
- Earnings per share (EPS)
- Price to earnings ratio (P/E)
- Projected earnings growth (PEG)
- Return on equity
- Dividend yield
- Dividend payout ratio
- Price to book ratio (P/B)
- Price to sales ratio (P/S)
- Current ratio
- Economic calendar
What are the advantages of fundamental analysis?
One of the most common investing approaches is fundamental analysis, which has several benefits. Primary research is attractive to investors for several reasons. It paints a more realistic image of the market’s current state, providing a precise indication of trading opportunities. There is a lot of uncertainty in the financial markets; therefore, fundamental research results aren’t always reliable.
Some of the key advantages include:
- Using fundamental analysis is a preferred method for long-term investments based on researching long-term trends.
- Fundamental analysis can be a profitable investment tool used to predict what investments will be the best, and these predictions are made far before an investor needs to decide on each investment.
- The more official and popular the news source, the more powerful it will affect the asset’s value.
- Earnings and expectations can offer insight into a company’s growth potential, allowing investors to pick the best companies and avoid any companies prone to shortfalls.
What are the disadvantages of fundamental analysis?
Making a conclusion using fundamental analysis could be time-consuming because gathering up-to-date information on an asset requires significant time and energy. Neglecting to consider the impact of market mood on prices is another drawback of this type of research, which could lead to missed profit chances.
Some of the key disadvantages include:
- Digging deep into financial reports, balance sheets, and cash flows is crucial but can be difficult for investors. These documents can also be falsified, which could result in a trader opening a lousy trade.
- When conducting technical analysis, there are clear signals about when to buy or sell, but fundamental factors don’t provide that luxury.
- Fundamental analysis is an in-depth approach to assessing currency price trends. It mainly applies to long-term investing, so many short-term trading strategies and objectives can’t rely on this analysis method.
- Traders will have to practice reasonable due diligence and have a solid understanding of the economy, the industry, and competitors within the industry they are researching. This process can be time-consuming, and the insights found may be useless when markets react quickly.
Applying the fundamental analysis to your trading
One way to begin incorporating fundamental research into your everyday trading is to pay close attention to the economic announcements scheduled for a specific week and evaluate them. The next step is determining which releases will most likely affect a particular currency pair. Using an economic calendar to check if these events have been labeled as high-impact releases is a straightforward identification approach.
Schedule your transactions according to the calendar and your expectations for whether the data fits analysts’ projections with this information. Looking at how a currency has performed in the past might give you a good idea of how it might react to economic releases in the future. The markets can go in any direction, so it’s essential to consider that possibility while making predictions. It would be best if you built contingency plans into your trading strategy to mitigate this risk.
Also, geopolitical events can have an impact on currency pairs; however, they can be hard to predict. Therefore, risk management, is critical when dealing with them.