Bitcoin Price Depends Upon What?
Bitcoin Price Depends Upon. Supply and demand are the market factors that determine the price of Bitcoin. As the number of vendors increases, the price tends to fall and vice versa. In contrast to fiat currencies like the US dollar, the UK pound, the euro, and the Japanese yen, Bitcoin (BTC) is a decentralized digital money that any official authority has never printed. A decentralized network of users and cryptographic protocols are necessary to create, store, and transfer Bitcoin.
A lack of intermediaries allows investors to conduct business deals directly. Trade barriers are eliminated, and the peer-to-peer Bitcoin network streamlines commerce. Launched in January 2009, the first cryptocurrency was proposed by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008.
The convenience and perceived worth of Bitcoin are enhanced by the increasing number of businesses that accept it. But, factors including media coverage, market mood, and regulatory news have caused its price to fluctuate rapidly, leading to considerable volatility.
Like the price of any other item or service, the value of Bitcoin is subject to the laws of supply and demand. When there are more purchasers than sellers, prices increase and vice versa. You should also know that, unlike stock exchanges, no one institution decides how much Bitcoin will cost or where to buy and sell it. Rather, the price is set by the individual market or exchange in response to factors like supply and demand and external ones like changes in regulations, security measures, and technology.
What Factors Could Impact Bitcoin’s Price?
The supply and demand for Bitcoin, competition from other cryptocurrencies, news, production costs, regulations, and the cost of production are some of the elements that affect Bitcoin’s price.
Supply and demand
According to the law of supply and demand, well-known to economists, an item’s market price and quantity are determined by the interplay between supply and demand. An economic good’s demand falls as its price rises and producers crank out more of it, and the inverse is also true.
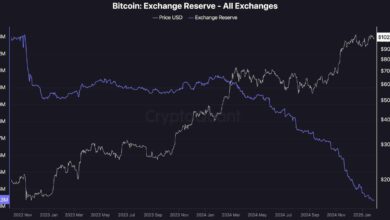
The basic economic theory of demand and supply is a key factor in the Bitcoin Price Depends Upon valuation. The digital currency known as Bitcoin is inherently scarce due to its hard cap of 21 million coins. Once that limit is reached, miners will no longer receive Bitcoin to validate transactions.
Similarly, every four years (roughly), an event known as the Bitcoin halving reduces the rate at which new Bitcoins (BTC) enter the market supply by half the reward for mining new blocks. Bitcoin prices have the potential to rise if supply growth slows and demand stays the same or even grows.
Competition and news
Numerous competing cryptocurrencies vie with Bitcoin for investors’ attention; some are Dogecoin (DOGE) and Ether (ETH), among many more. In addition, how the media portrays Bitcoin’s future possibilities can substantially affect investor sentiment, which in turn causes price volatility.
Cost of production
In addition to upfront expenditures like infrastructure and power for miners, there are indirect costs associated with the difficulty of the cryptographic problems miners must solve, which add up to the total cost of manufacturing Bitcoin. These expenses help set a floor, or “break-even” value, below which miners may question whether producing Bitcoin is still profitable.
The floor price is the lowest price at which Bitcoin mining becomes viable after accounting for operating costs. It is commonly referred to as the break-even point in Bitcoin mining. Additionally, the Bitcoin network controls the rate of Bitcoin creation by adjusting the complexity of its cryptographic puzzles about the total mining power. These changes have the potential to slow down or speed up the generation pace of Bitcoin, which in turn affects the total supply and, consequently, the market price of the cryptocurrency.
Regulation
Some nations are more accommodating to cryptocurrency than others; for example, El Salvador recognized Bitcoin as legal tender in 2021. China, on the other hand, officially outlawed cryptocurrency transactions in 2019. The market dynamics of Bitcoin Price Depends Upon are vulnerable to regulatory developments, which can cause uncertainty and potentially influence its price.
The price of Bitcoin can fall if governments impose restrictions on the cryptocurrency. On the flip side, more market participation and perhaps a rise in Bitcoin’s price could result from governmental initiatives that make the market more accessible, such as approving spot Bitcoin ETFs in the US and improved security measures.
Why is the Bitcoin Price so Volatile?
Bitcoin is an extremely volatile asset due to the lack of clarity surrounding its fundamental worth and the future price of BTC. The asset’s inflation rate falls over time as the number of new Bitcoin entering the supply slowly decreases every four years in the halving. Bitcoin is no longer an obscure asset; it has emerged as a major participant in the global financial system. CompaniesMarketcap ranks it as the tenth biggest asset by market cap as of this writing. In addition, it’s not just Bitcoin that causes media attention to outsize asset prices.
The instantaneous and pervasive nature of information in the modern day, made possible by digital and social media platforms, allows news stories—whether favorable or negative—to impact investor sentiment swiftly and, as a result, asset values globally. Cryptocurrencies are examples of extremely speculative markets where investor mood is key, increasing the impact of this effect.
The price of Bitcoin was greatly affected by the approval of U.S.-based spot Bitcoin ETFs on Jan. 11, which attracted institutional capital and increased demand. Consequently, conventional financial institutions and investors have flocked to buy Bitcoin, driving its price up 33% since January 11.
Layer-2 initiatives like the Lightning Network are addressing scalability and usability difficulties, which could boost Bitcoin’s value. Ethereum’s ERC-20 token standard enables smart contracts and tokens to be easily developed, but Bitcoin can’t handle them. Still, creative answers are popping up to make Bitcoin even more useful in this regard. One example is the RSK (Rootstock) platform, which is helping to close this gap in the Bitcoin ecosystem by integrating smart contract capabilities.
BRC-20 tokens are another unique technique to tokenize Bitcoin. BRC-20 is an experimental standard for creating, minting, and transferring fungible tokens, similar to ERC-20 on Ethereum and other Ethereum Virtual Machine networks.
How High can Bitcoin Realistically Go?
Many factors, such as market adoption, regulatory developments, technological advancements within the blockchain ecosystem, and overall economic conditions, can impact Bitcoin’s price trajectory, making predictions and speculation about its potential future price difficult.
Greater acceptance of Bitcoin for investments and transactions can drive demand, which is why market adoption is vital. Depending on whether they limit users’ freedom or provide them with security and transparency, regulatory acts taken by governments and financial institutions around the world can either aid or impede Bitcoin’s expansion.
Improving Bitcoin’s scalability, security, and use cases via technological breakthroughs can boost its value. In addition, inflation rates, currency devaluations, and investor sentiment toward traditional and digital assets are macroeconomic variables that could affect Bitcoin’s attractiveness as an investment.
Something else to think about is that Bitcoin Price Depends Upon is becoming increasingly known as a “digital gold,” making it a safe-haven asset and a store of value. This comparison highlights the potential of Bitcoin as a hedge against economic instability and shows how its digital form and finite quantity make it different from traditional investments like gold.
With all these factors in play, it’s hard to say how far Bitcoin could go. Historical trends have shown great volatility, with periods of strong price rises followed by periods of corrections. One way to predict Bitcoin’s future growth and acceptability is to use the technology adoption S-curve model. According to this model, Bitcoin will most likely follow the trajectory of past revolutionary technologies and acquire wider acceptability as it develops and overcomes initial adoption hurdles.
Final Thoughts
However, the theoretical maximum price of Bitcoin is very uncertain and subject to change based on developments in the field, as we have shown above. One should exercise caution when making predictions of Bitcoin’s price since, as with any investment, there is no assurance of a return.